Cyber attacks are often common in the internet world. Therefore, every second, we are at risk of losing our information. One of the most used methods today is the Man-in-the-Middle attack. Through this, the aim is to interfere with the communication between two or more devices, and thus obtain the data that is transmitted. However, with some recommendations, you can navigate without fear of becoming a victim of hackers.
What is a Man-in-the-Middle attack?
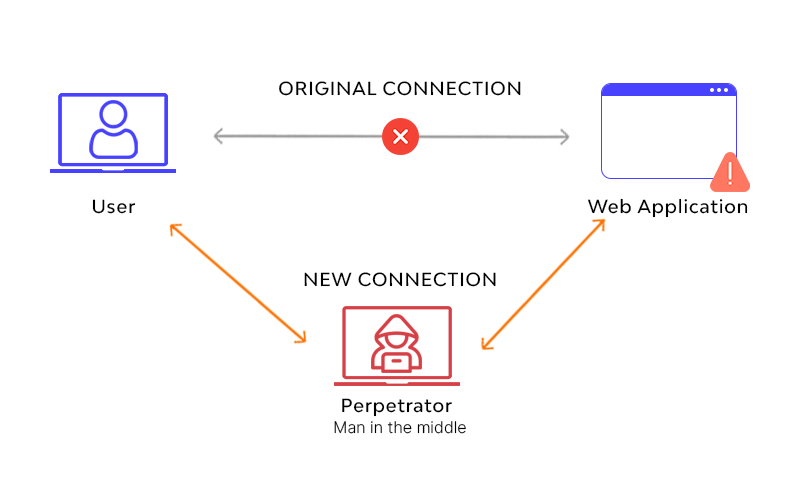
Every second we stay online we are at risk of a cyber attack. Among the most recognized, and which represent a warning, is the Man-in-the-Middle attack, also known as MitM or man-in-the-middle attack. It consists of a person or software interfering with communication between computers or devices, allowing a third party to have access to the information being transmitted. The idea of this attack is to divert data and control it.
The advancement of technology has also allowed the evolution of risks on the Internet. Previously, the hacker had to manipulate the physical channel to achieve communication interception. This is no longer necessary. The use of shared networks facilitates the process for a third party to carry out the MitM attack. Through this, the aim is to override the security protocols, in order to access the encrypted information of the communicating devices. Generally, these attacks tend to target online transactions where money is involved.
Types of Man-in-the-Middle attacks
The risk of suffering a MitM attack is latent at all times. The reality is that there is no single way to break into data communication. The hacker does not do everything by chance, he knows the victim to be able to implement the most appropriate method and deceive them. Types of Man-in-the-Middle attacks include:
- Attacks based on DHCP servers: When talking about DHCP, it allows you to dynamically assign an IP address and all its configuration. If a fake DHCP server is created, then it will take care of local IP address allocation control. With this, you will be able to divert and manipulate information traffic thanks to the fact that you are able to use gateways and DNS servers to your advantage.
- ARP cache poisoning: ARP or Address Resolution Protocol allows the resolution of IP addresses of a LAN network into MAC addresses. At the moment the protocol starts working, the IP and MAC addresses of the requesting machine are sent, as well as the IP of the requested one. Finally, the information is stored in the ARP cache. To gain access to this data, the hacker will then create a fake ARP. This will allow the attacker’s MAC address to be connected to the network’s IP and be able to receive all the information that is transmitted.
- Attacks based on DNS servers: the DNS or Domain Name System is in charge of translating domain names into IP addresses and storing them in a cache to remember them. The attacker’s idea is to manipulate the information in this cache, change the domain names, and redirect to a different site.
Types of decryptions in a MitM
Once the communication has been intercepted, the time comes when the data obtained must be decrypted. When it comes to Man-in-the-Middle attacks, attackers typically focus on four ways to gain access to information:
- HTTPS Spoofing: HTTPS is a protocol that ensures that the website you visit keeps your data secure. But a hacker has the ability to break this security. Installs a fake security root certificate. He tricks the browser into believing that the site is secure and allows him access to the encryption key. With this, the attacker will be able to obtain all the decrypted information and return it to the user without him noticing that he was violated.
- BEAST in SSL: in Spanish, it is known as SSL/TLS browser vulnerability. SSL and TLS are two other security protocols that seek to protect user information. In this case, the hacker takes advantage of the weaknesses of the block cipher to divert and decrypt each of the data sent between the browser and the web server. In this way, he knows the victim’s internet traffic.
- SSL Hijacking: When you enter a website, the browser first makes a connection with the HTTP protocol and then switches to HTTPS. This allows providing a security certificate, thus allowing the user to browse safely. If an attacker exists, then they will divert traffic to your device before the connection to the HTTPS protocol is achieved. This way you will be able to access the victim’s information.
- SSL Stripping – The attacker uses a MitM ARP cache poisoning attack. Through this, you will get the user to enter an HTTP version of the site. With this, you will have access to all the decrypted data.
Avoid a Man-in-the-Middle attack
Man-in-the-middle attacks pose a great risk to user information within the network. Therefore, it is always necessary to be alert and take measures to reduce the likelihood of an attack. The best recommendation is that you use a VPN, managing to encrypt our connection. Also, don’t forget to verify that once you enter the site it remains with HTTPS. If you switch to HTTP you may be at risk of attack.
And as for this protocol, if the website works only with HTTP, try not to enter it, since it is not considered secure. Also, stay up to date with all updates. Security methods are renewed every day to protect user information. Don’t forget to verify that the emails you receive come from secure addresses. By applying these recommendations you will reduce the risks.
